Copying files from a Terminal Services sessionWindows XP/2003 and greater support drive mapping back to the client workstation during a Terminal Services (Remote Desktop) session. This means you can copy files from the server to the client and vice versa. Each volume (removable, fixed or network) available on the client workstation is mapped (A for drive A:, C for drive C:, X for drive X: etc) and the remote Terminal Services session inherits the user's permission. So if you are logged on to the workstation as user A and you log in to the Terminal Services server as user B, the session will have access to the drives according to A's permissions. Using Mapped DrivesThere are several ways to access the mapped drives: Windows ExplorerWindows Explorer My Computer view shows the extra volumes: 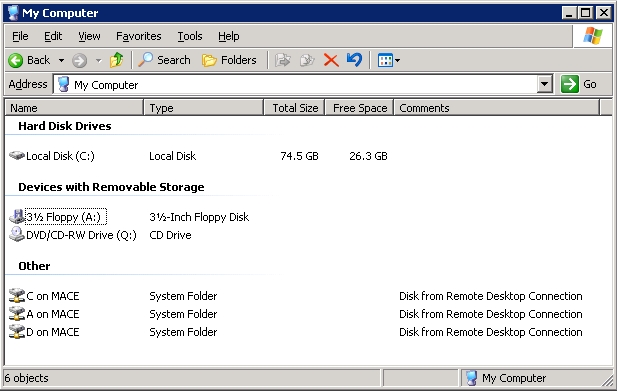 By double-clicking on the volume names as normal you can copy and paste files between the local drives and the remote drives. NET USE or UNC PathsDrives can also be mapped like a network drive. The client drives are accessible as \\TSCLIENT\C. Note the client workstation's machine name is not used, it is always referenced with the generic name TSCLIENT. So you can map a drive as follows: NET USE Y: \\TSCLIENT\D or simply use the Universal Naming Convention (UNC) syntax: COPY \\TSCLIENT\C\DATA\*.DOC Transfer SpeedThe speed the files transfer at is, of course, only as fast as the slowest connection speed available. For example, ADSL typically has a fast downstream (incoming) speed (eg 256kbps) but a slower upstream (outgoing) speed (eg 64kbps). When copying a file from one system to another, the file copy is “downstream” for one system and “upstream” for the other. So for two systems operating at 256/64kbps, the file will transfer at 64kbps. Another example is a server with a very fast connection, say 512kbps in both directions and a client with an entry level connection, say 256/64kbps. Copying a file from the server to the client will run at 256kbps (the client's downstream rate). But copying a file from the client to the server will only travel at 64kbps (the client's upstream rate). Workstation ConfigurationDrive Mapping works within the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) session so no special firewall settings or shared directories need to be assigned, either on the server or client. Existing shared folders are not accessible from the remote session. The special “shared folders” are accessible only within the remote session, they are not accessible on the LAN or Internet. Drive mapping requires: - The server must be running Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 or greater;
- The workstation must choose to share its drives as per the following:
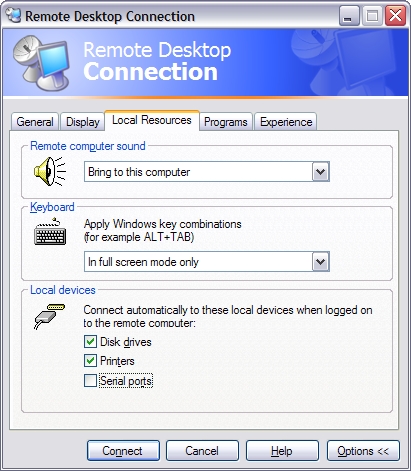
Server Configuration- The server must not have disabled Drive Mapping in Control Panel, Administrative Tools, Terminal Services Configuration, Connections, RDP-TCP (Properties):
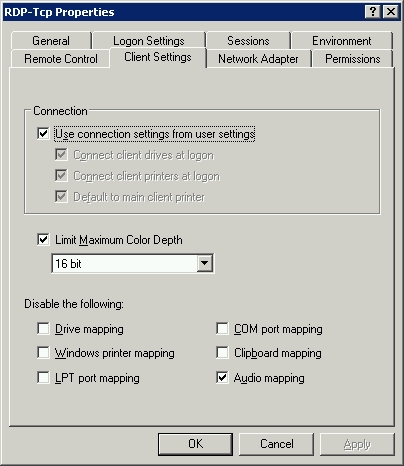
and, - The user must have been granted permission to access the shared drives:
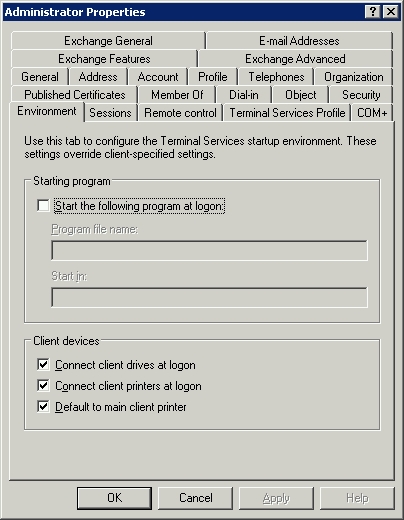
TroubleshootingDrive Letter Access (DLA) SoftwareIf the server has DVD/CD burning software installed, there may also be a Drive Letter Access (DLA) driver. DLA enables files to be written to the media using Windows Explorer by dragging and dropping. However, you may experience instability and crashes in svchost.exe if you connect using Remote Desktop with drive mapping enabled. Uninstall the DLA component using Control Panel → Add/Remove Programs. |