Windows Makes Static Noise/Clicks While Using MS-DOS ApplicationWhile using an MS-DOS application under Windows, the sound card may emit static, other random noise or clicks. This may happen if the audio card has been configured by Windows to use a CPU interrupt request (IRQ) of 3, 4, 5 or 7, and the MS-DOS application is polling the parallel ports and/or the serial ports (whether or not the machine itself has a parallel or serial port). This is because LPT1 and LPT2 (the parallel ports) most commonly use IRQs 7 and 5 and COM1 and COM2 (the serial ports) most commonly use IRQs 4 and 3. MS-DOS applications are generally hard-coded to communicate with the parallel and serial ports via their hardware addresses whereas Windows applications use the inbuilt software interfaces which separate the logical hardware from the physical hardware. Thus, if the hardware that is actually using an IRQ of 3, 4, 5 or 7 is not what the MS-DOS application expects, and if it happens to be the audio hardware, the audio hardware will emit random noise in response to the data the application is sending. To check if this is the case: - Click Start
 , type MSINFO32 in the search box and press Enter. , type MSINFO32 in the search box and press Enter. - Browse to Hardware Resources → IRQs:
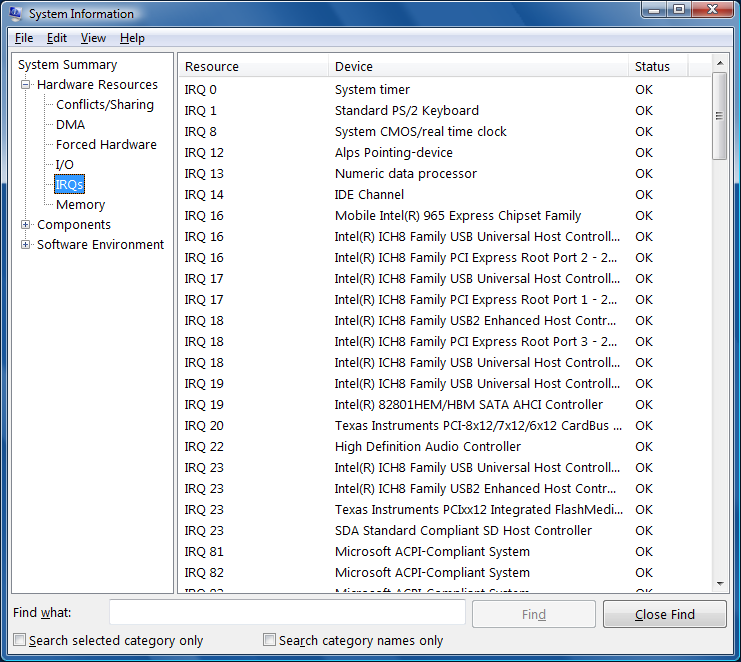 If there is audio hardware listed on IRQ 3 or 4, it means the MS-DOS application is sending data to the serial ports. If audio hardware is listed on IRQ 5 or 7, it means the application is sending data to the parallel ports. In the example above, the audio hardware is on IRQ 22.
Generally, because Windows takes control of the management of IRQs and other hardware resources, it is usually not a good idea (or even possible) to change them. However, upgrading the audio hardware's driver may correct the situation. Another possible remedy is, if the machine has a physical parallel port, to ensure it uses the IRQ. Modern Windows systems do not need to assign an IRQ to the parallel port, leaving it free for other devices. But it might help with this problem if the IRQ is occupied as MS-DOS applications expect. See the section titled “Parallel Port Settings” under Cannot print from MS-DOS application under Windows. Otherwise, mute the system when using the application. |