SBS 2008 Post-Setup Manual StepsMicrosoft Windows Small Business Server (SBS) 2008 usually requires some post-setup steps which are not covered by the setup wizards in the Windows SBS Console. Domains, IP Address & CertificatesThe use of a registered domain, static IP address and a certificate from a trusted certificate authority is highly recommended, and should be considered mandatory. Using dynamic IP addresses with a dynamic DNS service, and self-issued certificates is possible, but both configurations require much more manual attention, initially and over the life of the server. Additionally, having your own domain name is virtually mandatory with SBS. External Settings- If using an external name server provider for your domain, configure the “remote” alias as an A record, pointing to your site's IP address.
- Configure the Autodiscover records.
- Configure the MX with an A record. Don't configure the MX with a CNAME.
- Ensure the certificate you obtain contains the name remote.<domain>.
- If using a static IP address, ask your ISP to set up a reverse DNS pointer for remote.<domain> to your IP. (This step is not necessary if you are using an upstream smart host to route outbound email, but it's a good practice anyway in case you switch the configuration later.)
Updates & Software Installation- Apply latest Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack. (You may need to manually stop some services first.) Post-service pack Exchange Server rollups will be offered via Windows Update.
- Out of the box, SBS 2008 Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) does not support Windows 7/2008R2 and Windows 8/2012 clients. To remedy this, apply Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (which should be offered via Windows Update) and KB2828185/KB2938066 (which may need to be downloaded and applied manually).
- Install Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio. This is used to manage the various databases which are included with SBS 2008.
One-Off Post Installation Tasks- Set up forwarders in the DNS console. Specify your ISP or third party's DNS resolvers. (If not using third-party resolvers, it may be necessary to edit the registry as per KB968372.)
NB. Windows 2008 contains a cosmetic bug which means that “Use root hints if no forwarders are available” has the opposite effect that it implies. Ensure this is checked or unchecked as required. (It is suggested the option be unchecked, so that DNS will use the root hints in case the forwarders are down or cannot resolve a particular domain name.) - DHCP: Enable DNS Dynamic Updates & Extend Lease Time. Suggested settings as follows, but alter as required:
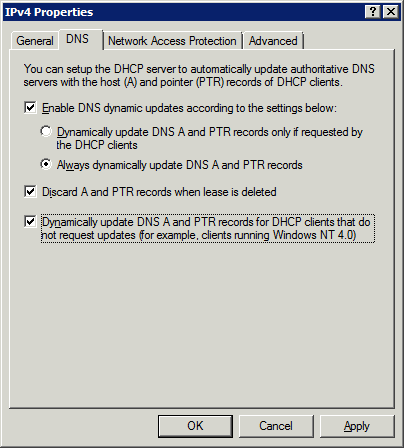 Extend the lease time to avoid a DCOM Error 10009 error and other IP address confusion as devices exit and re-enter the network. - Set workstation browser homepages. SBS 2008 imposes a policy which overrides each user's Internet Explorer homepage with http://companyweb. If this is not required, open Group Policy Management on the server, right-click Windows SBS User Policy under Forest: [Your Domain] → Domains → [Your Domain] and choose Edit. Then navigate to User Configuration → Policies → Windows Settings → Internet Explorer Maintenance → URLs → Important URLs. Disable or override as desired.
- Reserve TCP/IP Ports. By default, SBS 2008 has a lesser need to reserve listening ports to prevent them from being used as ephemeral (outbound) ports than earlier versions of Windows, but it is good practice to reserve some specific critical system ports, plus any additional ports required by your applications, to prevent connectivity problems that may arise later if the ephemeral port range is changed/expanded.
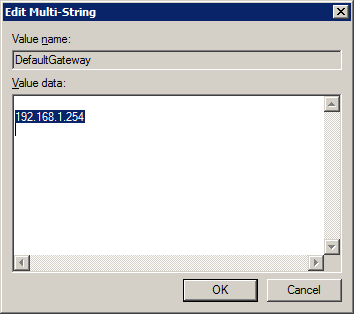
- Check Server's Gateway Setting. If you alter the server's IP address after the initial setup, the Gateway address may show as blank after each reboot. In turn this causes some services to not function properly, such as Terminal Services and DNS. To resolve, remove the blank line from the key DefaultGateway under HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\[SID] (where [SID] is the identifier of the network adaptor).
 - Tweak IIS 7. (1) The default setting in IIS 7 prevents opening the opening of any attachment with an ampersand (&) in the title in Outlook Web Access. This will need to be disabled if such documents need to be accessed.
(2) SharePoint has a default document upload limit of 200Mb but IIS 7 enforces a limit of 30,000,000 bytes so any document larger this cannot be uploaded. To increase the limit, open an elevated command prompt and enter: %windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd set config -section:requestFiltering -requestLimits.maxAllowedContentLength:209715200 (3) See Improving Encryption Quality on Windows-Based Webservers. - Increase Exchange 2007 Message Size Limits. Open the Exchange Management Shell and issue the following commands (assuming default SBS connectors and server name of <SERVER>):
Check and adjust global limits Get-TransportConfig | ft MaxSendSize, MaxReceiveSize Set-TransportConfig -MaxSendSize 100MB -MaxReceiveSize 100MB For sending messages Get-SendConnector | ft name, MaxMessageSize Set-SendConnector "Windows SBS Internet Send <SERVER>" -MaxMessageSize 100MB For receiving messages Get-ReceiveConnector | ft name, MaxMessageSize Set-ReceiveConnector "Windows SBS Internet Receive <SERVER>" -MaxMessageSize 100MB Set-ReceiveConnector "Windows SBS Fax Sharepoint Receive <SERVER>" -MaxMessageSize 100MB Set-ReceiveConnector "<SERVER>\Default <SERVER>" -MaxMessageSize 100MB To check limits on individual mailboxes Get-mailbox | ft Name, MaxSendSize, MaxReceiveSize, ProhibitSendQuota - Configure other domains. If the server needs to handle email for domains other than the default domain entered during setup, they must be configured under Exchange Management Console → Organization Configuration → Hub Transport → Accepted Domains.
- Configure non-local mailboxes. If the organisation has some mailboxes on the same domain as the default domain, but which are hosted elsewhere (such as POP account), change the properties of the domain under Exchange Management Console, Organization Configuration → Hub Transport → Accepted Domains from Authoritative Domain to Internal Relay Domain. This ensures that any Exchange users who email to a recipient with the same email domain which are not recognised by the server will be forwarded to the external smart SMTP host.
- Adjust Internal Databases. There are two SQL Server instances running in SBS 2008 by default:
\\.\pipe\MSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEE\sql\query — This contains the Sharepoint (Companyweb) and Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) databases. These should be configured to use the Simple recovery model so the transaction logs do not expand. The default Full Recovery model is not useful in most situations. If the server has been running for some time in Full Recovery mode, switch to Simple mode, backup the databases, and perform a manual shrink. Also, some of the databases under this instance may not be accessible through Management Studio because an Owner ID is missing. This can be corrected by running the following query against each database: USE [<Database>]
EXEC sp_changedbowner 'sa' .\SBSMONITORING — This contains the SBS logging database. It should already be set to Simple recovery but still requires manual intervention because it does not purge quickly enough, and can be slow due to missing indexes. See SBS 2008 Slow. - Adjust memory used by SQL Server for internal databases. See Sqlservr.exe Consumes Most of Memory in SBS 2008.
- Configure Windows 7/8 Workstations. Using Internet Explorer 10/11 on Windows 7/8 systems to access the Remote Web Workplace will not work due to a compatibility problem. See Cannot Use Remote Desktop on Remote Workplace.
- Add certificate to non-domain joined machines. If not using a trusted certificate, any systems which require access to Remote Web Workplace must have the server's certificate installed.
- Check Email Configuration. Use the service at https://www.mail-tester.com to test how your outbound email is treated by the outside world.
- Fix “The Terminal Services Gateway Service service is not running error” in Remote Web Workplace. KB2368713.
Regular Maintenance Tasks- Fix Backup Errors. Some servers need manual intervention to resolve backup problems. See SBS 2008 Backup Issues.
- Run WSUS Cleanup Wizard. This clears out superceded update files. If not run regularly, the WSUS system ends up with gigabytes of obsolete update binaries.
Open Windows Server Update Services, then <Server> → Options → Server Cleanup Wizard.  Note this process will not substantially reduce the size of the WSUS database itself. - Backup CompanyWeb. The SBS backup will backup Companyweb as part of the whole server backup, but if more control or granularity is required, the database can be backed up with the following commands:
cd /d "%ProgramFiles%\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\12\BIN" STSADM -o backup -url http://companyweb -filename "c:\backup\companyweb.bak" -overwrite - Clear SBS logs. Over a period of time the internal logs collected by SBS can grow to several gigabytes. If the server is running well, these can be cleared from time to time:
net stop DataCollectorSvc
cd /d "C:\Program Files\Windows Small Business Server\Logs"
del console.log
del MonitoringServiceLogs\*.* /s /q
net start DataCollectorSvc
del "C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\Logging\lodctr_backups\*.*" /s /q - Monitor system database sizes. Check the database and transaction log sizes at the following locations:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data
C:\Windows\SYSMSI\SSEE\MSSQL.2005\MSSQL\Data If you've switched the system databases to Simple mode (see above), these databases should not increase in size unduly. - Check & Renew Expired Certificates. Open Windows SBS Console, navigate to Network → Connectivity and run the Fix My Network wizard. This will reissue the self-issued certificate if it is expired or nearly expired.
|